Introduction
Gleevec, Imatinib mesylate, is the first in class BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor initially approved to treat CML. In February 2016, generic imatinib products became available. As generic products are not required to offer comparative efficacy and safety data, differences may arise. Small reports have found no significant differences in response durability and tolerability in patients transitioned from Gleevec to generic imatinib. Further, lower cost of generic products often influence treatment decisions and patient compliance. We sought to evaluate response durability, tolerability, financial costs, and adherence in patients with chronic phase CML (cpCML) who switched from Gleevec to generic imatinib and newly diagnosed cpCML patients initiated on generic imatinib.
Methods
We conducted a single-center, retrospective chart review of adult patients who received imatinib therapy for cpCML between June 1, 2015 to November 14, 2019. Patients who received ≥6 months of brand through the Specialty Pharmacy Service (SPS) at Atrium Health prior to switching to generic were included in Group 1 (Switch). Patients who initiated therapy with generic imatinib dispensed from SPS were included in Group 2 (New Start). Durability of response was described determined via peripheral blood BCR-ABL transcripts by PCR and reported major molecular response (MMR) after 12 months generic imatinib therapy. Additional factors characterizing the durability and tolerability of therapy included adverse effects due to drug, dose modifications, adherence rate, prescription cost per month, and frequency of switch between generic products.
Results
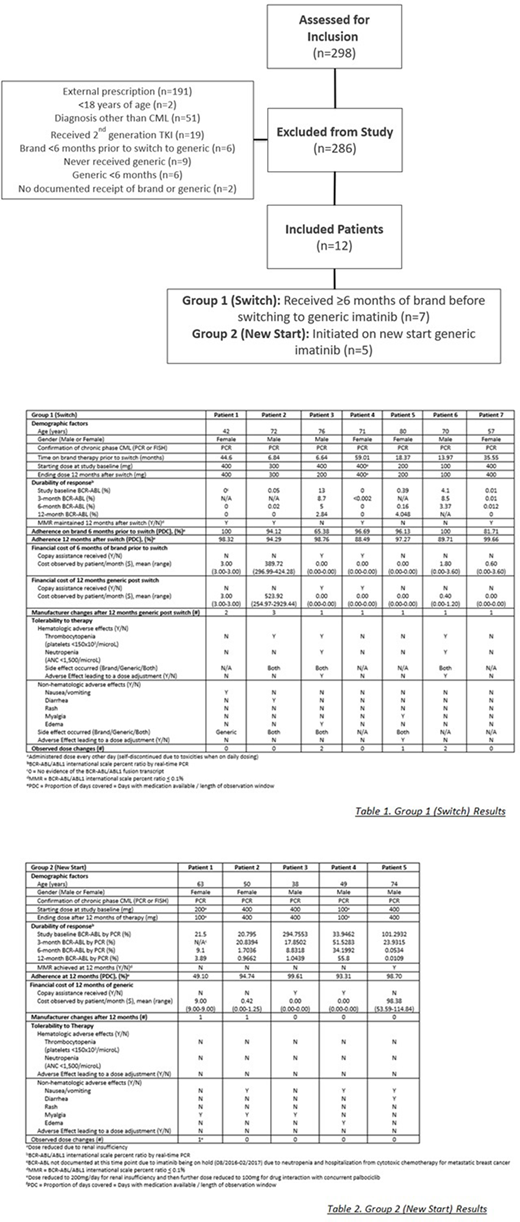
Of 298 patients assessed, 12 patients were evaluable. There were 7 Switch patients and 5 New Start patients. Figure 1. All 12 patients met WHO diagnostic cpCML criteria. No patients in either group had accelerated or blast phase CML, no patients received maintenance imatinib following allogeneic HCT.
In the Switch Group, 4 patients (57%) achieved MMR after 12 months of generic therapy. Of the 3 patients that did not achieve MMR, 1 patient relocated prior to 12-month assessment, 1 patient was noted to be non-compliant, and 1 patient had several treatment delays and dose reductions due to toxicities. 1 New Start patient achieved MMR at 12 months. Of those not achieving MMR, 1 was started on a reduced dose (100 mg /day) due to renal dysfunction, 1 had a PDC of 49.10% due to treatment delays while receiving treatment for a different malignancy, and 2 patients had logarithmic decreases in BCR-ABL but had not crossed the MMR threshold after 12 months of therapy. 5 Switch patients (71.4%) reported at least 1 adverse effect related to therapy, 3 of these (42.9%) required dose reduction. The adverse effects requiring dose reductions in the New Start patients included thrombocytopenia (n=2) and myalgia (n=1). All New Start patients reported at least 1 adverse effect with none of these patients requiring a dose reduction. Cost stayed the same or was reduced for 85.7% of the Switch patients, 1 patient experienced a cost increase and did not have co-pay assistance, and 2 patients received copay assistance. Cost of generic therapy was <$10/month in 85.7% of the Switch and 80% of the New Start patients. No patients experienced disease progression and PDC was >90% after 12 months on generic therapy for 71.4% Switch patients and 80% New Start patients. Table 1. and Table 2.
Conclusion
Patients with cpCML switched from brand to generic imatinib and patients newly started on generic imatinib appear to have durable responses and tolerance to generic imatinib. Dose reductions and non-adherence may have contributed to inadequate disease control in patients not achieving MMR in both groups. Patients switched from brand to generic imatinib may develop new side effects necessitating dose reduction. Thrombocytopenia may be more common in patients switched from brand to generic imatinib. Adherence to brand and generic imatinib is high and medication is affordable with most patients paying <$10/month. Our study is limited by a small sample size and retrospective nature. Prospective large studies are needed to compare tolerability and durability differences between brand and generic imatinib and available imatinib generic products.
Knight:Foundation for Financial Planning: Research Funding. Ai:Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Speakers Bureau. Grunwald:Premier: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; Janssen: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Forma Therapeutics: Research Funding; Forma Therapeutics: Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy; Premier: Consultancy; Trovagene: Consultancy; Trovagene: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Trovagene: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Cardinal Health: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy; Cardinal Health: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Cardinal Health: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Research Funding; Premier: Consultancy; Genentech/Roche: Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Research Funding; Forma Therapeutics: Research Funding. Avalos:Juno: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Best Practice-Br Med J: Patents & Royalties: receives royalties from a coauthored article on evaluation of neutropenia. Copelan:Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Chojecki:Novartis: Other: Investigator Meeting Attendance; Incyte: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.